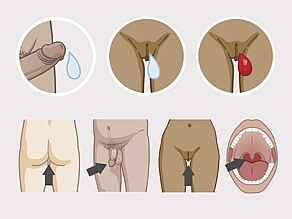
Someone can get HIV through body fluids of people who already have HIV. HIV can be transmitted through:
Infected semen, vaginal fluid and menstrual blood can enter your body via the mucous membrane of the anus, glans of the penis, vagina and mouth.
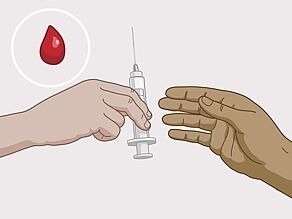
Infected blood can reach your blood directly by sharing used injection material or through blood transfusion.
Transmission through blood transfusion almost never happens in Europe, because the blood is tested for HIV.
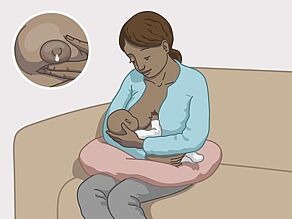
Finally, HIV can also be passed on through breast-milk when breast-feeding.
Transmission through sex
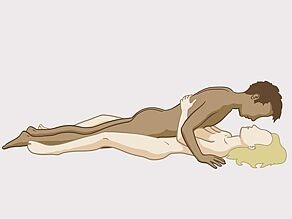
- Through vaginal sex or anal sex without a condom with someone who has HIV.
- There is only a very small risk of getting HIV through oral sex (if semen or blood from a person with HIV gets into your mouth and you have broken skin there).
With the right treatment, an HIV-positive person can hardly pass on HIV when having sex without a condom.
Transmission in other ways
- From mother to child during pregnancy or delivery or when breast-feeding. With the right treatment, women with HIV can have healthy children.
- By sharing used injection material with someone with HIV.
- Through blood transfusion. This almost never happens in Europe, because the blood is tested for HIV.
No transmission through casual contact
You cannot get HIV through casual contact, for example: by sharing a glass or plate with someone who has HIV or by touching or kissing each other.
It is not possible to know if someone has HIV by looking at him or her.
Protection against HIV
People with HIV can infect others if they do not get treatment. Many people do not know they have HIV. To protect yourself, use condoms during sex.