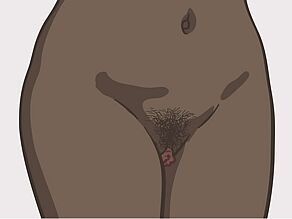
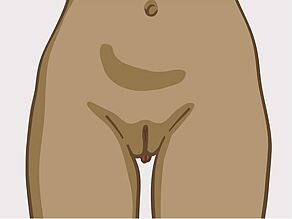
The visible (outer) sexual organs in women are also called female genital organs or the vulva.
They include:
The urinary meatus and the anus are not sexual organs.
Every woman's vulva looks different. The appearance of the vulva is not important for its function.
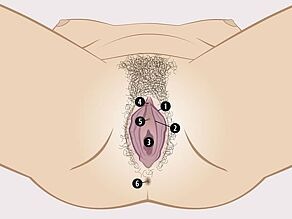
Labia and the entrance to the vagina
The labia are lip-like skin parts. They protect the vagina, the clitoris and the urinary meatus.
Women have two pairs of labia:
- The outer labia: These are usually covered with hair and thicker than the inner labia.
- The inner labia: These are not covered with hair and thinner than the outer labia. They may be larger or smaller than the outer labia.
Some women have internal labia that protrude beyond the external labia. Other women have internal labia that are completely covered by the external labia. How they look is not important for their function.
The entrance to the vagina lies between the inner labia.
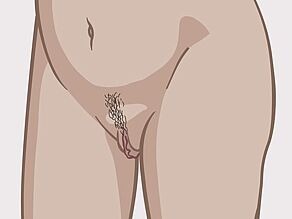
Clitoris
The clitoris is a very sensitive organ above the opening of the urethra. The clitoris lies at the point where the inner labia come together at the mons pubis.
The visible part of the clitoris is approximately the size of a pea. Sometimes the visible part is also smaller or larger. The clitoris has two long columns that extend inside the body: the corpus cavernosum. These columns form the largest part of the clitoris. They are located under the skin and are not visible. The two clitoral columns extend up to the outer labia.
The clitoris is the woman's most important organ for sexual arousal. For many women, touching or stroking the clitoris will lead to orgasm.
In some countries in Africa and Asia the clitoris of girls and women is cut off. This is called female genital mutilation. Female genital mutilation is prohibited in Germany and in Europe.